Battery Technologies
Today, there are many different types of batteries - from disposable alkaline batteries to rechargeable lead-acid batteries, nickel-based batteries, and lithium-ion batteries. Lithium ion batteries are the most popular battery on the market today due to their reliability, high energy density, and low maintenance.
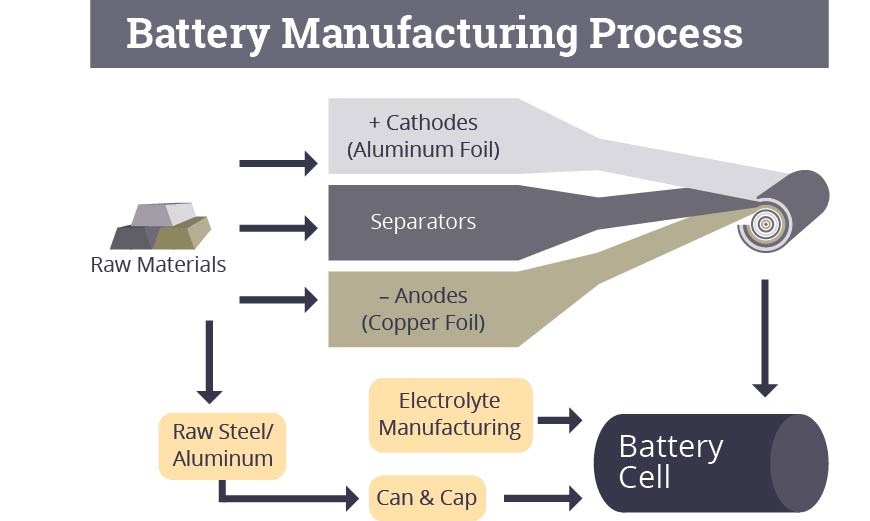
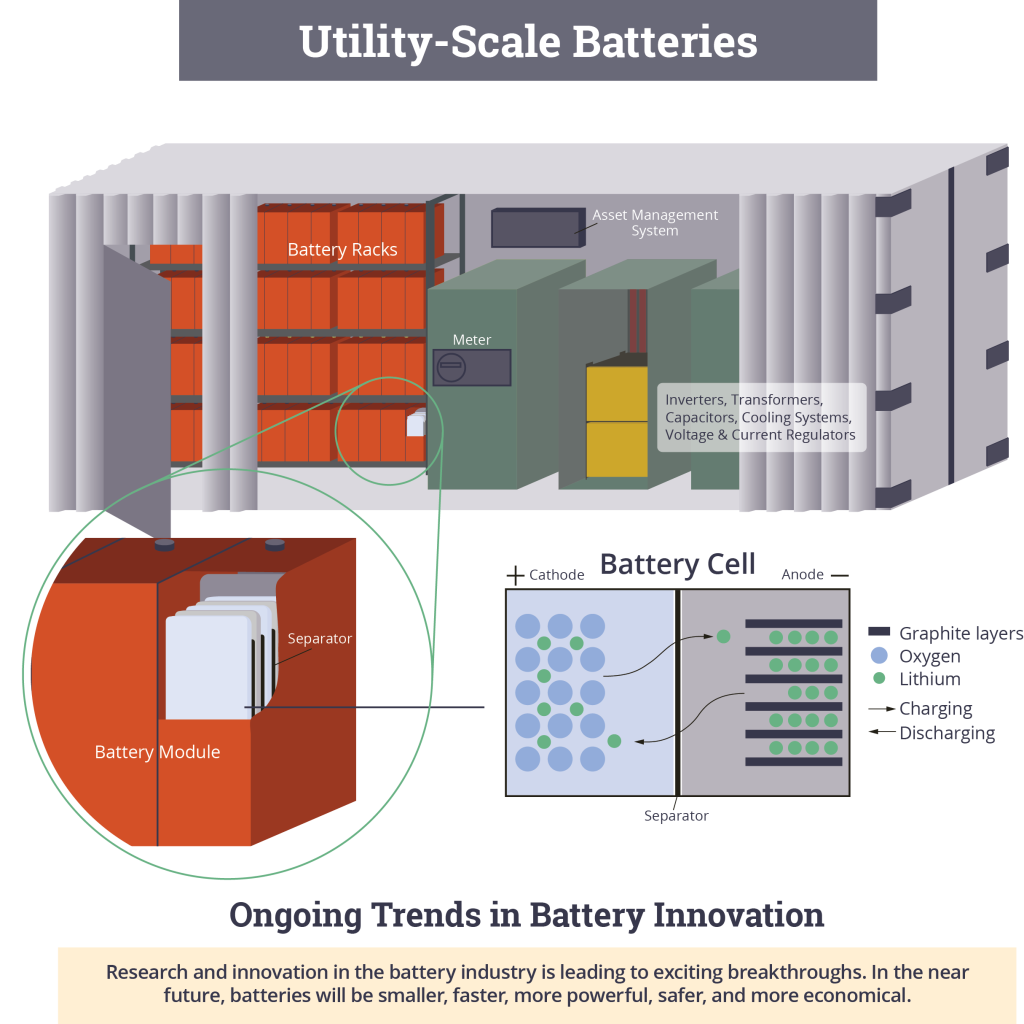
Batteries are composed of three major components – the cathode, the anode and the electrolyte – that store electrical energy in the form of chemical energy and can convert chemical energy back into electricity.
Battery systems use multiple batteries to store large amounts of energy. The batteries can be stacked and bundled together in modules to form customized energy storage solutions.
Battery Systems Can Be Used In Various Settings
Batteries can be located anywhere and do not require extensive land use or maintenance. They do not pollute the air or make excessive noise, which makes them ideal for dense urban areas where clean, invisible power is needed. Batteries can be applied at different scales, including residential, commercial, and utility. Homeowners are using residential battery systems for back-up power and to complement solar systems, while business owners are using commercial-scale batteries to help reduce energy and demand charges on their electricity bill. Utilities are being driven toward large-scale battery systems to regulate and stabilize the electric grid through frequency regulation and fast-reacting responses to increased electricity demands. With utility-scale batteries, the grid can “bank” excess electricity generated when demand is low to use when demand is higher.
Benefits of Utility-Scale Batteries
Utility-scale batteries provide a wide range of services to the grid and are a fuel-agnostic system optimization tool; batteries can be used with any type of electricity generation, from coal to natural gas to wind. If deployed properly, utility-scale batteries save money for electricity customers. Additionally, batteries act as a multipurpose tool for the grid by:
- Creating efficiencies in grid operation
- Providing ancillary services, such as frequency and voltage regulation and fast demand response
- Reducing investment in transmission upgrades and peaker plants
- Improving reliability of electricity delivery to customers
- Maximizing solar and wind integration by reducing the intermittency of these resources
Rising Global Demand
Innovation, increased understanding of the benefits of the technology, and cost reductions are motivating significant growth in market demand for utility-scale batteries. The utility-scale energy storage market and the residential and commercial energy storage markets are all expected to grow over the next decade. Global revenues in the utility-scale battery sector are projected to grow from $231.9 million in 2016 to $3.6 billion by 2025. In the global residential and commercial markets, installed energy storage capacity is expected to grow seventy-fold from 2014 to 2024. In the United States, a five-fold increase in the size of the energy storage market is expected in the next half-decade, growing to a $2 billion market in 2020.
Battery Costs are Falling
Battery costs have been decreasing steadily in recent years, due to advances in manufacturing, technology innovation, economies of scale, and increased competition. Experts estimate that the cost of batteries will decrease by 80 percent of 2014 prices within the next five years. System costs for battery energy storage for electricity systems are projected to drop to $230/KWh by the early 2020s, which would make them cost comparative with the average household electricity bill.
Career Opportunities in the Utility-Scale Battery Sector
Utility-scale battery deployment and manufacturing require a variety of professions, including:
- Sheet metal worker
- Computer hardware engineer and technician
- Electrical engineer and technician
- Software developer
- Chemical engineer and technician
- Production manager and technician
- Truck driver
- Electrical power line installer and maintenance worker