Types of Solar Power Technologies
There are two ways to harness solar energy: solar photovoltaic (PV) and solar thermal. PV panels are commonly seen on rooftops but can be scaled to the utility level. PV panels absorb energy from sunlight to generate electricity. Solar thermal panels, on the other hand, capture solar energy as heat. Simple rooftop solar thermal systems collect heat from the sun and transfer it to another source, often a water heater. At the utility level, Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) systems generate electricity by using a series of precisely angled mirrors to concentrate sunlight to heat oil, which is used to boil water and create steam that turns a turbine, generating electricity.
Rising Demand Across the Globe
Global solar photovoltaic (PV) installed capacity has increased by a factor of nearly 70 over the last decade, from 2.6 GW in 2004 to 177 GW in 2014. As a result of this growth, investment dollars are flooding the market, prices are falling, and the industry is undergoing a period of rapid innovation.
In the United States, solar PV cells are a primary source of new electricity generating capacity. In the first half of 2015, solar represented 40 percent of all new electricity generating capacity. Strong demand has made the United States the world’s fifth largest solar market in terms of installed capacity. Forecasts show significant growth continuing through 2030.
Falling Costs of Solar Power
According to current projections, solar power will not only soon reach grid parity, but will also surpass fossil fuel competitors in cost efficiency. The cost of solar per kilowatt-hour is forecast to be cheaper than coal and natural gas within the next 5 to 10 years. Experts predict that the cost of solar in the U.S. will continue to fall over the next 15 years for utility, commercial/industrial, and residential PV.
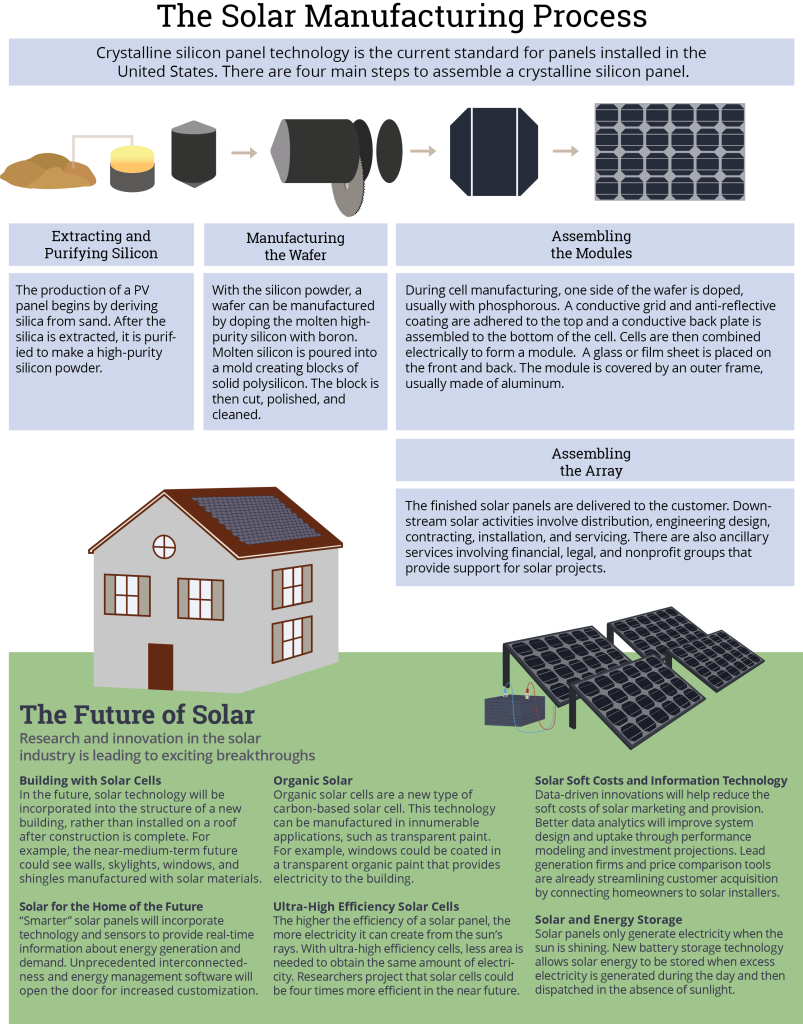
Manufacturing Solar Panels
Manufacturing, installing, and maintaining the solar panels needed to meet the increasing demand for solar energy will create thousands of good-paying jobs in the U.S.
Career Opportunities in the Solar Industry
The solar industry includes scientists, engineers, and various workers in manufacturing, construction, and installation. Electricians, plumbers, and solar PV installers work in solar installation, which is the fastest-growing portion of the solar industry. Other solar manufacturing positions include, semiconductor processors, computer-controlled machine tool operators, electrical and electronic equipment assemblers, and industrial production managers. Engineers, especially chemical, electrical, and materials engineers, are in high demand within the solar industry.